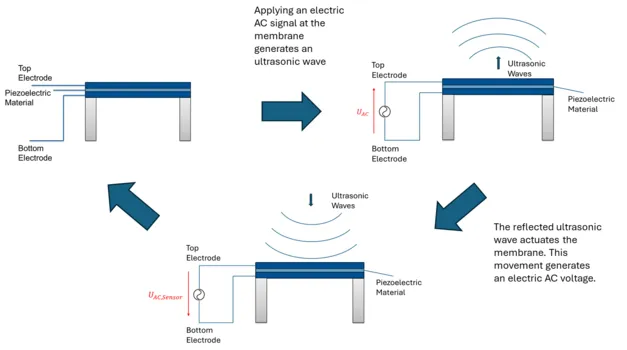
Piezoelectric ultrasound transducers (PMUTs) for ultrasonic imaging and particle trapping
Piezoelectric Micromachined Ultrasound Transducers (PMUTs) have garnered significant attention in recent years due to their potential for enhancing medical imaging and particle manipulation. These devices utilize the piezoelectric effect to convert electrical energy into mechanical vibrations, generating high-frequency ultrasound waves. Compared to traditional ultrasound wave generation methods, PMUTs offer several notable advantages, including easy integration into CMOS technology, lower power consumption, and reduced production costs.
In this project, we are developing membrane-based transducer concepts using thin-film piezoelectric materials (see Figure 1). The project involves several tasks: defining the design of the devices with the aid of computer simulations, fabricating the devices, and conducting final characterization. We explore various aspects of the manufactured components to gather information about material properties, device performance, and system-level behavior. Additionally, we investigate the potential for device- and system-level optimization for specific target applications. Our project focuses on two key use cases for the PMUTs: medical imaging and particle manipulation.
- Medical Imaging:
- High-Resolution Imaging: PMUTs enable the generation of high-frequency ultrasound waves, resulting in improved spatial resolution compared to conventional ultrasound transducers. This enhanced resolution allows for the visualization of finer details within biological tissues.
- Miniaturized Imaging Systems: The compact size of PMUTs enables their integration into minimally invasive medical devices, such as endoscopes and catheters. This facilitates real-time imaging during procedures, providing valuable guidance to surgeons and interventionalists.
- Particle Manipulation:
- Acoustic Tweezers: PMUTs can generate acoustic forces that can be used to manipulate microscopic particles, including cells and biomolecules. This technique, known as acoustic tweezers, allows for precise control over the position and orientation of particles.
- Cell Sorting: PMUT-based acoustic devices can be used to sort cells based on their physical properties, such as size and density.
- Drug Delivery: PMUTs can be used to generate acoustic forces that can deliver drugs to specific target sites within the body.
The project is funded by the BCDC (Bayrische Chip Design Center) and is a cooperation between TUM and EMFT at Frauenhofer.